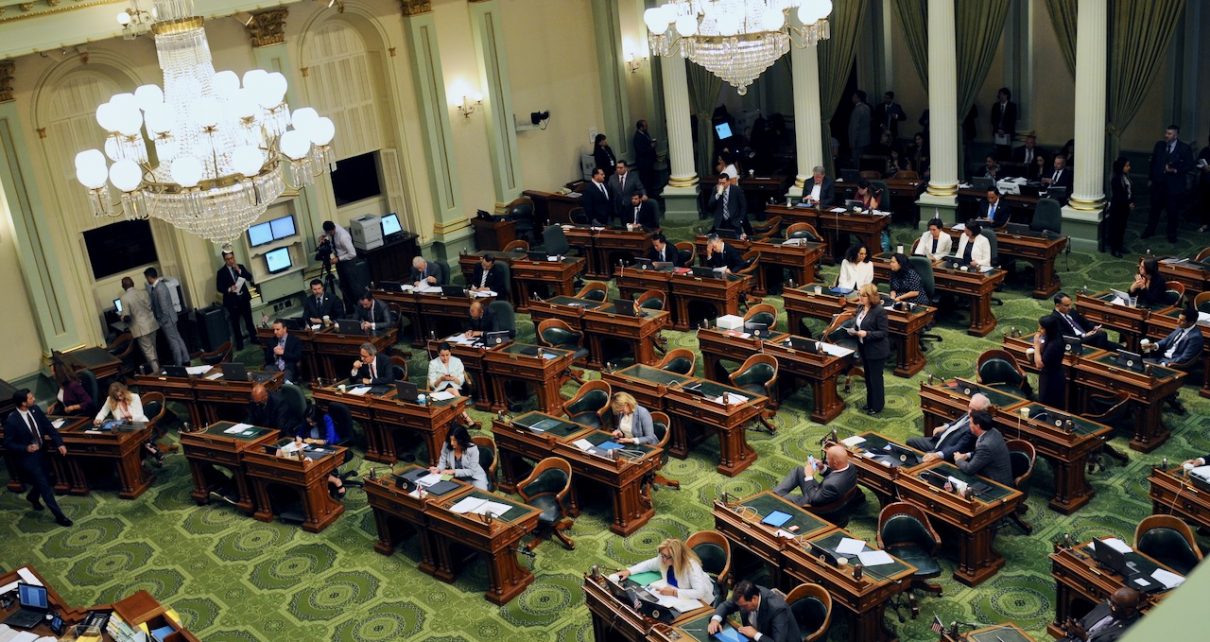
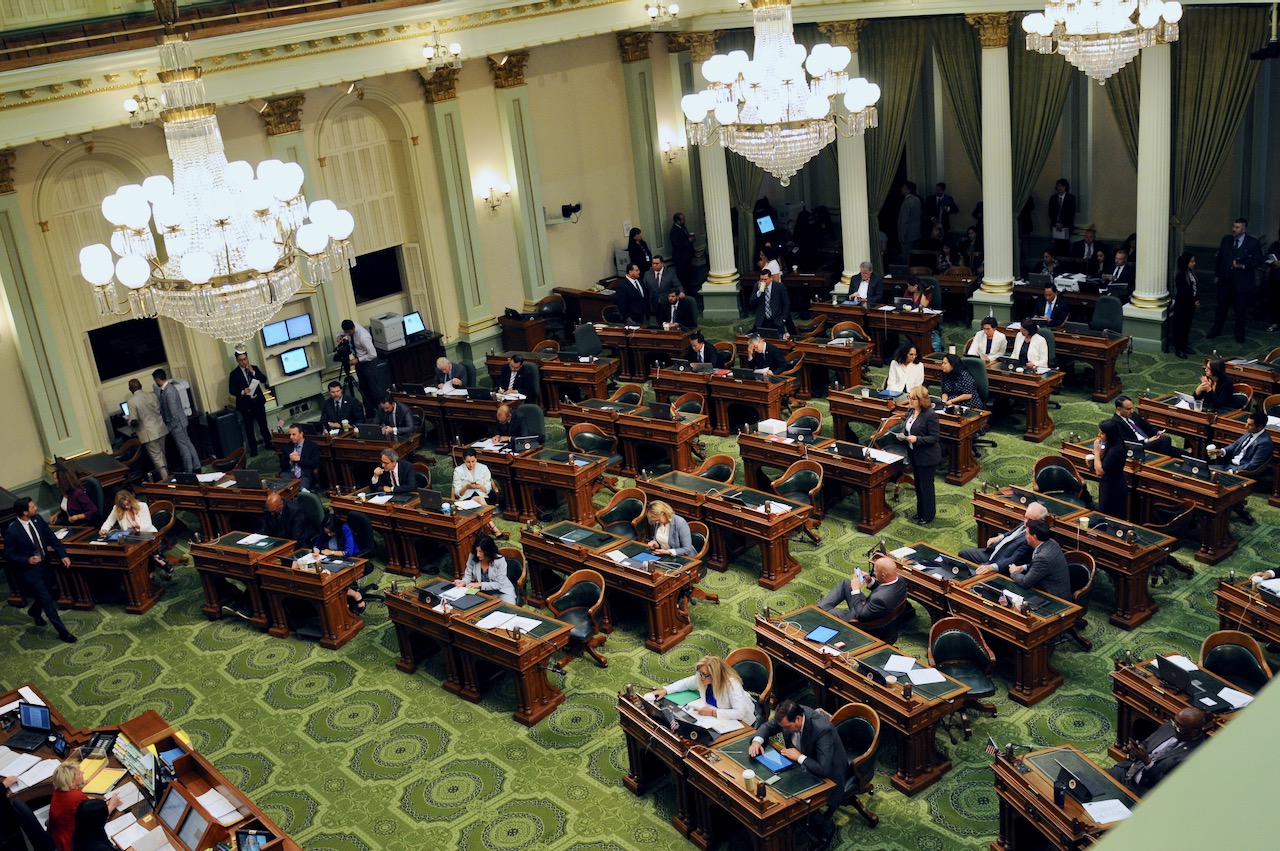
California State Assembly Chamber. (Photo: Kevin Sanders for California Globe)
Legislative Powers and Duties by Statute
Assembly and Senate each have their set of rules
By Chris Micheli, January 1, 2020 8:00 am
In California’s Government Code, there are several code sections that set forth legislative powers and duties. These statutes were added by Proposition 24 in 1984 and are found in Title 2, Division 2, Part 1, Chapter 8, Article 2. The provisions of law are summarized below:
Speaker of the Assembly – Gov’t Code Sec. 9910
The Speaker is responsible for the efficient conduct of the legislative and administrative affairs of the Assembly. The Speaker is elected upon organization of the Assembly at the beginning of each regular or special session and serves until adjournment sine die of that session, unless removed and a successor is chosen.
Assembly Committee on Rules – Gov’t Code Sec. 9911
There is the Assembly Committee on Rules, which consists of the Speaker, who is the chairman of the committee, and six other Members of the Assembly, three to be elected by the party having the largest number of Members in the Assembly and three to be elected by the party having the second largest number of Members.
The Assembly Committee on Rules has a continuing existence and may meet and act during sessions of the Legislature or any recess and in the interim periods between sessions. The committee has all the powers and authority provided in Article IV, Section 11 of the Constitution.
Powers of the Assembly Committee on Rules – Gov’t Code Sec. 9912
The Assembly Committee on Rules has the power to assign all bills to Assembly committees; appoint the Chairmen and Vice-chairmen of all other Assembly Committees (who must be members of different parties); have general direction over the Assembly Chamber and rooms set aside for the use of the Assembly, including private offices; allocate all funds, staffing, and other resources necessary for the effective operation of the Assembly; exercise such other powers and perform such duties as may be provided by statute.
Neither the Chairman nor any member or agent of the Assembly Committee on Rules has the power to perform any action on behalf of the committee including, but not limited to, the making of contracts, the payment of claims, the allocation of office space, or the hiring or dismissal of staff, without the express authorization of two thirds of the total membership of the committee.
Appointments by the Assembly – Gov’t Code Sec. 9913
All statutory appointments delegated to the Speaker of the Assembly are subject to confirmation by the Assembly Committee on Rules, two thirds of the membership concurring.
President pro tempore of the Senate – Gov’t Code Sec. 9914
The President pro Tempore is elected upon organization of the Senate at the beginning of each regular or special session and serves until adjournment sine die of that session, unless removed and a successor chosen.
Senate Committee on Rules – Gov’t Code Sec. 9915
There is the Senate Committee on Rules, which consists of the President pro Tempore of the Senate, who is the chairman of the committee, and four other Members of the Senate, two to be elected by the party having the largest number of Members in the Senate and two to be elected by the party having the second largest number of Members.
The Senate Committee on Rules has a continuing existence and may meet and act during sessions of the Legislature or any recess and in the interim periods between sessions. The committee has all the powers and authority provided in Article IV, Section 11 of the Constitution.
Powers of the Senate Committee on Rules – Gov’t Code Sec. 9916
The Senate Committee on Rules has the power to assign all bills to Senate committees; appoint the Chairmen and Vice-chairmen of all other Senate Committees (who must be members of different parties); have general direction over the Senate Chamber and rooms set aside for the use of the Senate, including private offices; allocate all funds, staffing, and other resources necessary for the effective operation of the Senate; exercise such other powers and perform such duties as may be provided by statute.
Neither the Chairman nor any member or agent of the Senate Committee on Rules has the power to perform any action on behalf of the committee including, but not limited to, the making of contracts, the payment of claims, the allocation of office space, or the hiring or dismissal of staff, without the express authorization of two thirds of the total membership of the committee.
Joint Rules Committee – Gov’t Code Sec. 9917
There is the Joint Rules Committee which is comprised of the combined membership of the Assembly Committee on Rules and the Senate Committee on Rules and two other Members of the Senate, one to be elected by the party having the largest number of Members in the Senate and one to be elected by the party having the second largest number of Members.
The committee created has a continuing existence and may meet and act during sessions of the Legislature or any recess and in the interim periods between sessions. The committee has all the powers and authority provided in Article IV, Section 11 of the Constitution of California.
Any action of the committee requires an affirmative vote of not less than a majority of the Senate members and a majority of the Assembly members of the committee, except that any action which involves or anticipates the expenditure or allocation of funds requires an affirmative vote of at least two thirds of the Senate members and two thirds of the Assembly members.
- Conservation Banks - February 22, 2026
- Mergers of Unincorporated Associations - February 21, 2026
- A Historic Look at Bill Introductions in the California Legislature - February 21, 2026